#Calcium content in cashew nuts
Calcium content in cashew nuts
Calcium content in cashew nuts
I. Cashew nuts contain no calcium? How much calcium is in cashews?
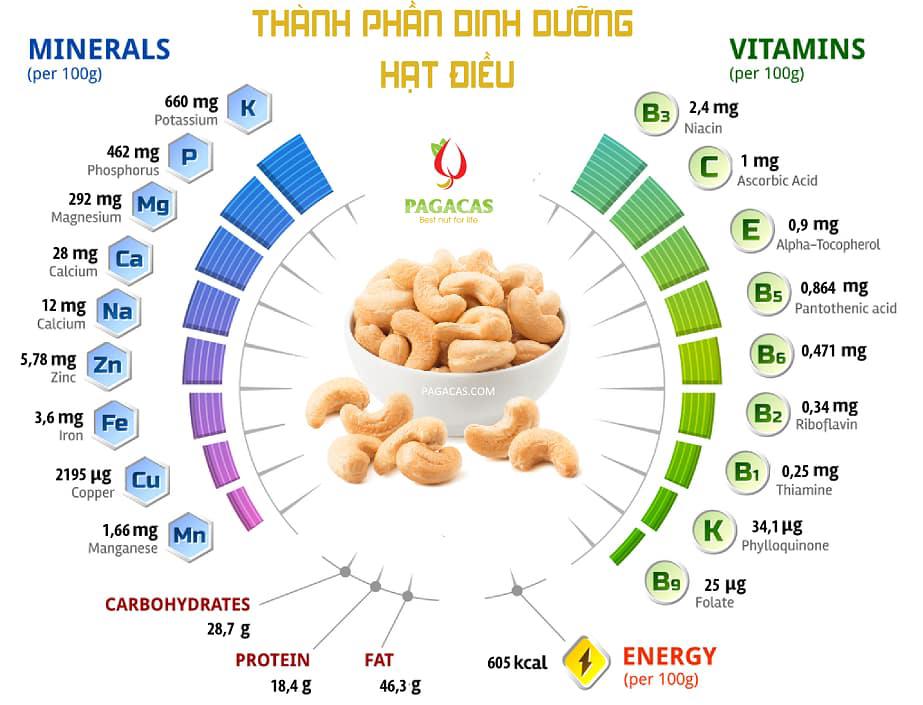
Cashew nuts do contain calcium, but not in very high amounts1. One ounce (28 grams) of cashews contains about 10 milligrams of calcium2. While this isn't a significant source of calcium compared to dairy products or fortified foods, it still contributes to your daily intake.
Cashew nuts do contain calcium, although the amount is relatively small compared to other sources like dairy products or leafy greens. To break it down:
Calcium Content in Cashews:
-
One ounce (28 grams) of cashews: Contains about 10 milligrams of calcium.
Nutritional Benefits of Cashews:
-
Healthy Fats: High in monounsaturated fats, which are good for heart health.
-
Protein: Provides a decent amount of protein for muscle repair and growth.
-
Magnesium: Important for muscle function, with about 83 mg per ounce.
-
Antioxidants: Contains vitamins E and K, which help protect your cells from damage.
-
Copper: Essential for iron absorption and red blood cell formation, with about 0.6 mg per ounce.
While cashews aren't a major source of calcium, they still offer a wide range of nutrients that contribute to a balanced diet. If you're looking to increase your calcium intake, consider combining cashews with other calcium-rich foods like almonds, kale, broccoli, or dairy products.
II. What is calcium?

Calcium is a very important mineral for the human body. It accounts for about 1.5 - 2% of body weight, with 99% of calcium found in bones, teeth, and nails, and 1% in the blood.
Roles of calcium:
-
Bones and teeth: Calcium combines with phosphorus to form the basic structure of bones and teeth, making them strong.
-
Neuromuscular activity: Calcium is necessary for muscle contraction and the functioning of the nervous system.
-
Blood clotting: Calcium plays an important role in the blood clotting process.
-
Heart function: Calcium helps regulate heart rhythm and the function of the heart muscle.
A lack of calcium can lead to issues such as osteoporosis, nervous system weakness, and cardiovascular problems. In children, calcium deficiency can cause rickets and developmental issues.
III. Effects of calcium on the body
Calcium plays a pivotal role in several critical bodily functions:
-
Bone and Teeth Health: Calcium is the primary building block for bones and teeth. It's essential for the formation, strength, and maintenance of skeletal structures.

-
Muscle Function: Calcium is crucial for muscle contractions. When a nerve stimulates a muscle, calcium is released, helping the muscle cells contract.
-
Nerve Transmission: Calcium ions are involved in neurotransmitter release, allowing nerve cells to communicate effectively with each other.
-
Blood Clotting: Calcium is essential in the blood clotting process, helping prevent excessive bleeding when you're injured.
-
Heart Health: It plays a role in maintaining proper heart rhythm by helping with the contraction of heart muscles.
-
Cell Function: Calcium assists in various cellular functions, including signaling and maintaining cell structure.
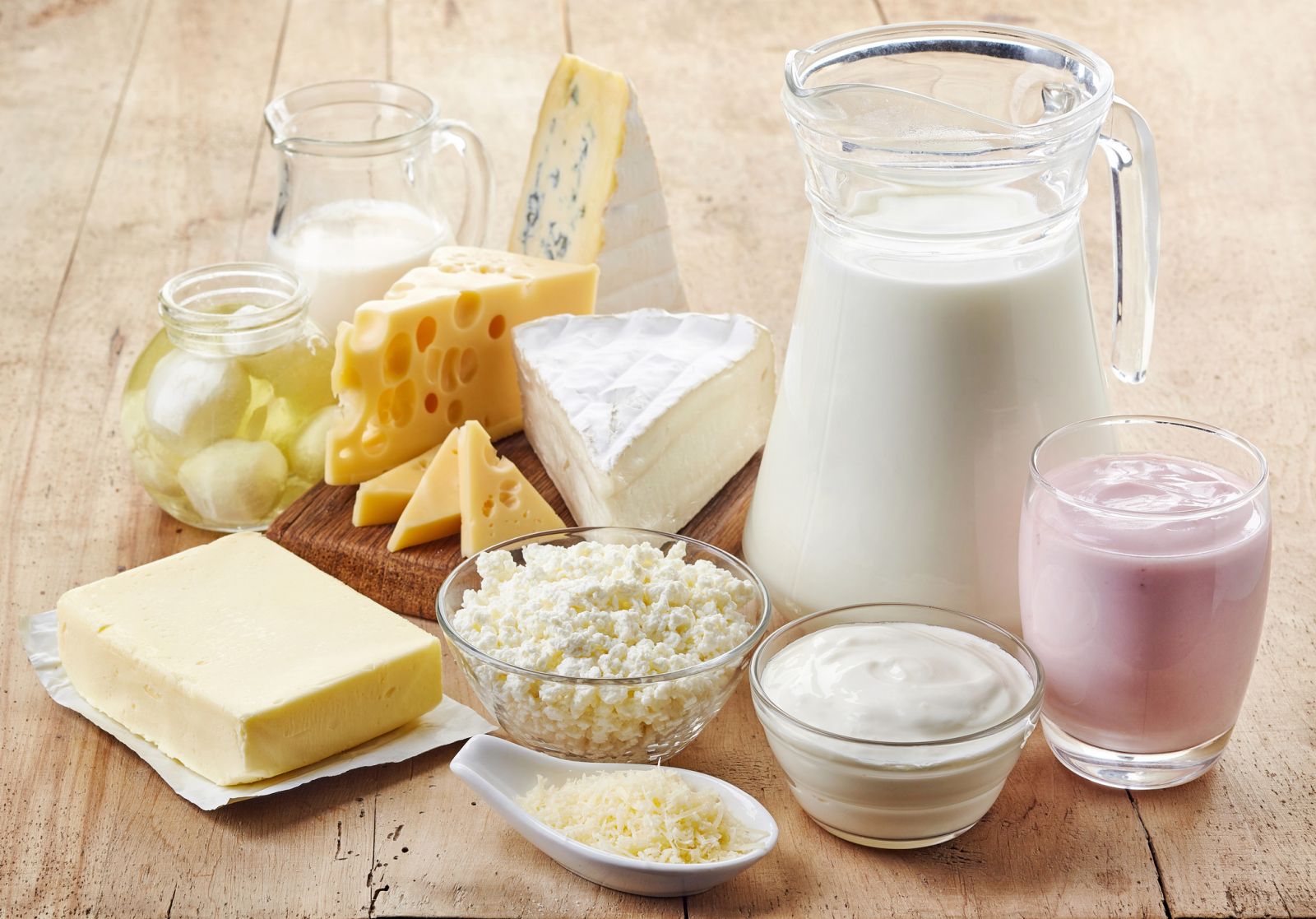
Calcium Sources:
-
Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, yogurt.

-
Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, collard greens.
-
Fortified Foods: Certain cereals, orange juice.
-
Fish: Especially those with edible bones like sardines and salmon.
-
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds.
Maintaining an adequate intake of calcium is vital for overall health, particularly for preventing osteoporosis and ensuring proper physiological function.
IV. How should cashews be used with your diet to supplement the appropriate amount of calcium?
Cashews are not a primary source of calcium, but they can still contribute to your daily calcium intake when combined with other calcium-rich foods. Here are a few suggestions for incorporating cashews into your diet:
-
Snacking: Use cashews as a healthy snack. They provide good fats, protein, and a bit of calcium.

-
Smoothies: Add cashews to your morning smoothie to boost nutrition and enhance flavor.
-
Salads: Sprinkle crushed cashews on salads for added crunch and nutrition.
-
Cashew Milk: Use cashew milk as a dairy substitute. While it doesn't have as much calcium as soy or almond milk, it's still a nutritious option.
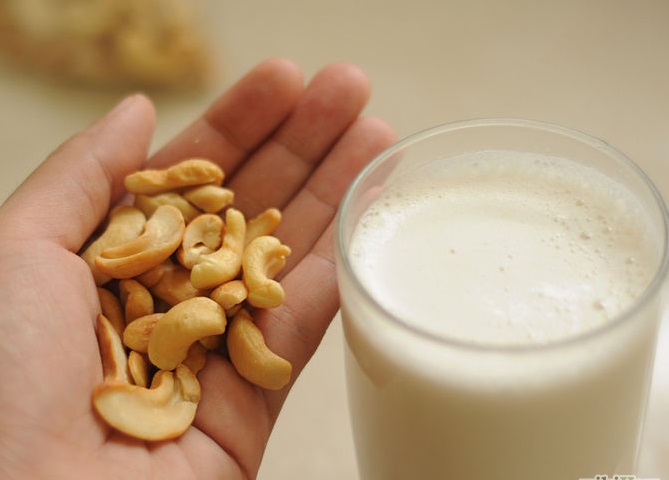

-
Cooking: Incorporate cashews into stir-fries, curries, or pasta dishes to enhance flavor and nutrition.
To boost calcium intake, pair cashews with other calcium-rich foods such as:
-
Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and bok choy.

-
Fortified Foods: Certain cereals and plant-based milks.
-
Dairy Products: If you're not avoiding dairy, use cheese, yogurt, and milk.
A balanced diet that combines multiple sources of calcium will help you meet your daily calcium needs.
Xem thêm: Hạt điều có chứa canxi không? Lượng canxi trong hạt điều là bao nhiêu
Learn more: Do Cashews Contain Calcium? How Much Calcium Is In Cashews?

 Brian Dương
Brian Dương

TVQuản trị viênQuản trị viên
Xin chào quý khách. Quý khách hãy để lại bình luận, chúng tôi sẽ phản hồi sớm